 Solar energy is one of the best green technologies
Solar energy is one of the best green technologies
I. Introduction to Green Technologies
A. Defining Green Technologies
Green technologies, sometimes called greentech, are the application of science and technology to the development of ecologically friendly goods and services. Through encouraging sustainable practices and protecting natural resources, these technologies seek to lessen the detrimental effects of human activity on the environment.
Innovations in green technologies include everything from energy-efficient appliances to sustainable farming methods and renewable energy sources like solar and wind power.
B. Importance of Sustainable Solutions
One cannot emphasize the need for sustainable solutions enough. The quick speed of climate change and environmental deterioration demands quick action to lessen these problems.
To this end, green technologies provide an essential first step. We can reduce waste, use fewer fossil fuels, and protect natural resources by implementing sustainable methods and technologies. Significant economic and social ramifications accompany this, in addition to its environmental advantages.
Green technologies are important because they can:
1. Reduce greenhouse gas emissions:
Green technologies like solar and wind power can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a decrease in global warming.
2. Conserve Natural Resources:
Recyclables and composters are examples of sustainable practices that help protect natural resources for future generations.
3. Create Jobs and Stimulate Economic Growth:
Particularly in the renewable energy and energy efficiency areas, the green technology industry is generating new employment possibilities and promoting economic growth.
4. Improve public health:
Green technology can raise public health and standards of living by reducing pollution of the air and water.
Ultimately, a sustainable future depends on green technologies. These creative fixes will help us to improve public health, lower our environmental impact, protect natural resources, and promote economic prosperity.
II. Key Features of Green Technology
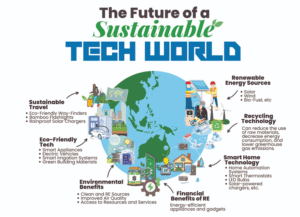
1. Environmental Focus:
By lowering waste, pollution, and carbon emissions, green technology seeks to preserve the environment and natural resources. It looks to stop more damage and undo prior environmental damage.
2. Sustainable Energy:
Green technology stresses the use of environmentally friendly renewable energy sources such as geothermal, wind, and solar energy. These are becoming more and more economical and effective substitutes.
3. Recycling and Waste Reduction:
Recycling is an important component of green technology since it reduces waste and reuses materials, helping to conserve resources. This covers recovering precious resources from electronic waste and car parts in addition to recycling metal, glass, paper, and plastics.
4. Carbon Capture and Storage:
Among the green technologies is the creation of carbon capture systems that seek to extract and store greenhouse gases from the atmosphere, either at the combustion site or from the atmosphere itself.
5. Innovations in Agriculture:
Green technology also includes sustainable agriculture methods like organic farming and developments in livestock feed. These techniques lessen farming’s and livestock’s environmental effects.
6. Investment and Adoption:
Globally, green technology has attracted substantial investment and adoption; many businesses and governments now include environmental sustainability into their objectives and policies. Significant funds for green technology are included in the US $1.2 trillion Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, for instance.
7. Challenges and Considerations:
Though there are many advantages to green technology, there are also drawbacks, such as the demand for rare minerals and the possible environmental effects of some technologies, such as the extraction of lithium for electric car batteries.
Examples of Green Technology
Solar Power:
With photovoltaic solar panels that can turn sunlight into electricity, solar energy is one of the most popular and affordable green technologies.
Electric Vehicles:
Another instance of green technology are electric automobiles, which provide a greener substitute for conventional fossil fuel-based cars, including hybrid and fully electric models.
Smart Homes and Appliances:
The Internet of Things (IoT) enables smart homes and appliances with energy-saving capabilities, allowing users to track and reduce their energy consumption.
Cloud Computing:
Virtual servers, data duplication reduction, and resource sharing to reduce hardware waste can all help cloud computing become more energy-efficient.
III. Different Types of Green Technology in 2024
1. Solar Energy:
Solar energy harnesses the power of the sun to generate electricity or heat. This includes solar panels, solar water heaters, and solar cookers.
2. Wind Energy:
Wind energy uses wind turbines to generate electricity. This includes onshore and offshore wind farms, wind-solar hybrids, and wind-diesel hybrids.
3. Hydro-Energy:
It harnesses the power of moving water to generate electricity. This includes hydroelectric power plants, tidal power plants, and wave power plants.
4. Biomass Energy:
Biomass energy uses organic matter to generate electricity or heat. This includes biofuels, biogas, and bio-oil.
5. Geothermal Energy:
Geothermal energy harnesses the heat from the Earth’s core to generate electricity. This includes geothermal power plants and geothermal heating systems.
6. Green Building:
Green building refers to the design and construction of buildings that minimize environmental impact. This includes energy-efficient systems, sustainable materials, and waste reduction.
7. Sustainable Agriculture:
Sustainable agriculture practices minimize environmental impact by reducing water and fertilizer usage, promoting biodiversity, and using organic farming methods.
8. Recycling:
Recycling involves the reuse and recycling of materials to conserve natural resources and reduce waste. This includes recycling of plastics, glass, paper, and metal.
9. Carbon Capture and Storage:
Carbon capture and storage involves capturing carbon dioxide emissions and storing them underground or utilizing them in other ways.
10. Electric Vehicles:
Electric vehicles use electricity from renewable sources to power transportation, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
11. Smart Grids:
Smart grids use advanced technologies like IoT and AI to optimize energy distribution and consumption, reducing energy waste and improving efficiency.
12. Green Transportation:
Green transportation includes alternative modes of transportation like cycling, walking, and public transportation, as well as electric and hybrid vehicles.
13. Waste Management:
Waste management involves the reduction, reuse, and recycling of waste to minimize environmental impact and conserve natural resources.
14. Sustainable Water Management:
Sustainable water management involves the efficient use and conservation of water resources, reducing waste and pollution.
IV. Advantages of Green Technologies
A. Environmental Benefits
1. Reduced carbon footprint:
Benefits:
Because green technologies use renewable energy sources like solar and wind power and boost energy efficiency, they help cut carbon emissions. In doing this, climate change is diminished, and the effects of human activity on the environment are lessened.
Examples:
A switch to green technology like wind turbines and solar panels can drastically cut carbon emissions. By substituting new LED lights for outdated lightbulbs, CA Technologies, for example, cut their lighting energy use by 50%.
2. Preservation of Natural Resources:
Benefits:
Green technologies lower waste and the requirement for ongoing raw material extraction, therefore helping to preserve natural resources. This guarantees that the natural resources on earth will be sustainable over time.
Examples:
One way to save natural resources and lessen the need to plant new trees is to recycle cardboard. Reusable water bottle use also lessens the amount of plastic trash produced.
B. Economic Advantages
1. Cost Savings in the Long Run:
Benefits:
Because green technologies use less energy and require less maintenance, they frequently result in large long-term cost savings. The illustration of this is solar panels, which, over time, can pay for themselves through energy savings.
Examples:
Over time, solar panels can save money and lower energy bills. Furthermore, businesses like CA Technologies reduced their energy costs by using LED lighting.
2. Job Creation in the Green Sector:
Benefits:
The green technology industry is driving economic growth, job creation, and a sustainable future. Among these are positions in environmentally friendly manufacturing, sustainable agriculture, and renewable energy.
Examples:
Examples include the expanding green technology industry, which is generating new employment in sectors including eco-friendly manufacturing, sustainable agriculture, and solar and wind energy.
C. Social Impact
1. Improved Public Health:
Benefits:
Green technology encourages pure air and curbs air pollution, which enhances public health. In metropolitan settings where air pollution is a major health issue, this is especially crucial.
Examples:
Pollution can be lower and air quality improved via smart buildings and sustainable urban planning. The green technology industry, with innovations like wind turbines and solar panels, not only fosters economic growth and sustainability, but also reduces air pollution by replacing polluting fossil fuels.
D. Community Engagement:
Benefits:
Green technologies engage communities in sustainable practices and promote environmental awareness. This fosters a sense of responsibility and encourages individuals to contribute to environmental sustainability.
Examples:
Participating in local sustainable agriculture projects and recycling programs among other green initiatives, raises community knowledge of the environment and encourages participation in sustainability initiatives.
These benefits of green technology emphasize their enormous advantages in terms of social impact, economic growth, and environmental sustainability.
V. Challenges and Limitations of Green Technologies
Green technologies have many obstacles and restrictions that need to be resolved, even if they have enormous potential to build a more sustainable future. Principal concerns include:
A. Initial Costs and Investments
The expensive initial outlay for implementing green technologies is one of the main barriers to their broad acceptance.
Many times, switching to environmentally friendly solutions calls for large expenditures in infrastructure, research, and development. Smaller firms in particular may find it difficult to justify the upfront expenses, even with the long-term environmental advantages.
B. Technological Limitations
The reliability and efficiency of some green technologies are still lower than those of conventional ones.For instance, there are weather-dependent and sporadic renewable energy sources like solar and wind. Energy storage options, such as batteries, to deal with intermittency are still developing and have capacity, cost, and environmental limitations.
C. Policy and Regulatory Issues
Inconsistent or insufficient rules can hamper green technologies. The encouragement of companies and people to use environmentally friendly practices requires clear and encouraging rules. A good regulatory framework could make it unnecessary and difficult to develop and apply green technologies. Still more restrictions consist of:
- New technology integration: logistical issues in supply chains and infrastructure as it stand
- little public knowledge and instruction on the advantages of green technologies
- Resource intensity in several green technologies’ manufacture, including solar panels and electric cars
- Electronic trash (e-waste) management issues related to the recycling and disposal of components of green technology
- International collaboration and setting of green technology common standards
It will take coordinated efforts from governments, companies, and individuals to overcome these obstacles. Realizing the full potential of green technology and guaranteeing a sustainable future require addressing budgetary limitations, enhancing technological efficiency, and developing supportive legislative frameworks.
VI. Innovations in Green Technologies
A. Breakthroughs in Renewable Energy
1. Next-Generation Solar Panels:
Perovskite Solar Cells:
The efficiency levels of these inexpensive, flexible, and lightweight solar cells are on par with those of conventional silicon solar cells. Applications for them are many and include portable gadgets and solar windows.
Floating Solar Farms:
These creative methods have the dual benefit of producing electricity and conserving water by using bodies of water for solar panels. Lakes, reservoirs, and even the open sea can all have them deployed.
B. Advancements in Wind Turbines:
1. Larger and More Efficient Turbines:
More electricity is being produced, and dependency on fossil fuels is being reduced with the development of larger and more efficient wind turbines. This covers improvements to turbine materials, design, and installation methods.
2. Offshore Wind Farms:
Huge clusters of turbines erected in the water, where the wind is stronger and more consistent than on land, are known as offshore wind farms. Utilizing this powerful wind, offshore farms can generate a large amount of electricity, which lowers greenhouse gas emissions and our dependence on fossil fuels.
C. Sustainable Materials and Manufacturing
1. Biodegradable Plastics:
Plant-based Packaging:
An environmentally friendly substitute for conventional plastic, which greatly contributes to plastic trash and microplastics in our oceans, is plant-based packaging.
Companies like Avantium are manufacturing polyethylene furoate (PEF), a 100% recyclable and biodegradable plant-based plastic, exclusively using bio-based feedstocks like sugars taken from agricultural waste.
2. Green Chemistry in Industry:
Circular Economy:
Reusing, repairing, and recycling of materials and products is promoted by the circular economy idea to cut waste and resource use. For the circular economy to be possible, green technology solutions develop new recycling methods and business structures.
Biotechnology:
Biotechnology: Sustainable agriculture, biofuels, and biodegradable materials are all made possible by biotechnology. By use of genetic engineering and synthetic biology, more robust and resource-efficient crops are being created.
D. Digital Solutions for Sustainability
1. Internet of Things (IoT) in Energy Management:
Smart Buildings and Appliances:
Artificial intelligence and smart technology integration can maximise energy efficiency and the efficacy of green solutions in appliances and buildings.
Demand Response Systems:
Real-time adjustments to energy demand made possible by these systems guarantee that supply matches demand. In doing so, energy waste is decreased and energy distribution is optimized.
2. Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency:
Traceability and Transparency:
Blockchain technology offers a safe and decentralized way to monitor the provenance, origin, and sustainability credentials of goods, hence improving supply chain transparency. All along the supply chain, this supports sustainable behaviors and accountability.
Advancements in digital solutions, sustainable materials, and renewable energy are paving the way for a greener future.
VII. Case Studies and Success Stories
A. Green Cities and Urban Planning

1. Copenhagen’s Green Initiatives:
Bike-Friendly Infrastructure:
With almost 62% of its population utilizing bicycles as their main form of transportation, Copenhagen has made significant investments in bike-friendly infrastructure. Both carbon emissions and traffic jams have greatly decreased as a result.
Renewable Energy:
By 2025, Copenhagen hopes to be carbon-neutral, and it has invested heavily in solar panels and wind turbines.
Waste Management:
Waste going to landfills is minimized, and recycling is given first priority in Copenhagen’s incredibly effective waste management system.
2. Masdar City’s Sustainable Infrastructure:
Green Buildings:
Masdar City has green buildings made to use as little energy as possible and to let in as much natural light. City buildings are going green with wind turbines and solar panels.
Public Transportation:
Masdar City offers a thorough public transit system that includes a tram network and electric buses. Walking and cycling are some alternate forms of transportation that the city promotes.
Water Management:
In order to cut water waste and the city’s water footprint, Masdar City has put in place cutting-edge water management technology, including greywater reuse and rainwater collection.
B. Corporate Sustainability Efforts
1. Tesla’s Impact on the Automotive Industry:
Electric Vehicles:
The general market can now afford and access electric cars, thanks in large part to Tesla’s contribution to their popularisation. This has helped to significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions from the car industry.
Tesla has also made significant investments in wind turbines and solar panels to power its production sites and lower its carbon footprint.
Sustainable Manufacturing:
Tesla has minimized trash and recycled as part of its sustainable production methods to lessen its environmental impact.
C. Google’s Renewable Energy Commitments:
1. Renewable Energy:
Google has committed heavily to renewable energy, funding solar and wind projects to power its offices and data centres. This has lessened both its dependence on fossil fuels and carbon footprint
2. Energy Efficiency:
Along with adopting LED lighting and maximizing server usage, Google has also put energy-efficient procedures into its data centers and offices.
3. Sustainable Operations:
To lessen its environmental impact, Google has put into place sustainable operating techniques such as recycling and waste minimization.
These success stories and case studies demonstrate how crucial green projects and corporate sustainability programs are to lessen environmental effects and advance a more sustainable future.
VIII. Conclusion: Embracing a Greener Future
A fundamental idea in environmental management, sustainability includes social, economic, and environmental components. The ecosystem, natural resources, and the effects of climate change must all be preserved.
People can choose environmentally friendly transportation, save water, and use less electricity. Employing renewable energy sources, putting energy-efficient procedures into place, and giving sustainable supply chains first priority are ways that businesses may lead the charge for sustainability.
Creating an informed society requires knowledge and education about environmental concerns. Networks of long-lasting changemakers are created and creativity is fostered by cooperative efforts. Our combined embrace of sustainability will help to build a healthier, greener future for coming generations.
FAQs
What are the most promising renewable energy sources today?
Solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy are now the most promising renewable energy sources. As wind energy spreads, solar energy becomes more and more efficient and economical.
The constant and clean energy output of geothermal energy is making it more and more popular than hydroelectric energy.
How can individuals contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle?
By forming easy habits like using public transit, conserving water, and consuming less energy, people may help to promote more sustainable living. By adopting the three R’s—reduce, reuse, and recycle—they may likewise cut waste. People may also back environmentally friendly companies and campaigns.
What are the economic incentives for businesses to go green?
Going green can help companies save money, improve the standing of their brand, and reach new customers. Significant financial reductions are possible with green technologies by lowering waste and energy use.
Companies that use sustainable business methods can also draw in investors and customers who are concerned about the environment, which will improve their standing and ability to compete.
What role does government policy play in promoting green technologies?
Green technology is greatly advanced by government policy, which sets rules, offers incentives, and funds R&D. Governments can incentivize companies to use green technologies with grants, subsidies, and tax breaks. Regulations promoting sustainable practices and lowering emissions are another power they have.
Are green technologies scalable for widespread adoption?
The scalability of green technology for broad use is growing. The efficiency and economy of renewable energy sources have increased with technological advancements.
Governments and commercial entities are also making substantial investments in green technologies, which promote their development and use. Green technologies are becoming more and more accessible and reasonably priced for broad use as the need for sustainable solutions rises.




Explore the captivating images in this collection – there is something to delight every viewer! Whether your preference is based on outdoor or indoor pictures, versions showcasing their poses or feelings, you will find a plethora of visuals to enjoy. Feel absolve to peruse through the edited, whimsical, individual, and team shots too. Naked Grannies Website blend is guaranteed to create a smile to that person!
[…] emphasis on green construction technologies fits its aspirational target of reaching net zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by […]
Your site visitors, especially me appreciate the time and effort you have spent to put this information together. Here is my website Article Star for something more enlightening posts about Data Mining.
[…] the cons, such as intermittency and high upfront costs, also need to be addressed through continued technological advancements and policy […]
[…] and environmentally friendly economy. Continued research, development, and deployment of these technologies are essential for achieving long-term climate goals and creating a healthier planet for future […]
As someone still navigating this field, I find your posts really helpful. My site is 59N and I’d be happy to have some experts about Thai-Massage like you check it and provide some feedback.
[…] rely on diverse alternatives, such as electricity, hydrogen, and renewable fuels. The urgent need to reduce transport-related emissions serves as the fundamental force for change, with a consensus that integrating all viable alternatives will […]
[…] emphasis on green construction technologies fits its aspirational target of reaching net zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by […]