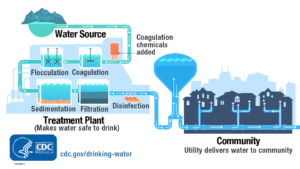
 Water Treatment and sanitation process in general (courtesy CDC)
Water Treatment and sanitation process in general (courtesy CDC)
I. Introduction
1. Overview of the relevance of water treatment and sanitation
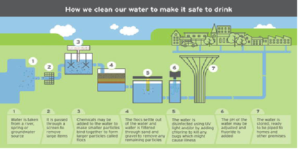
Access to safe drinking water and adequate sanitation is vital to public health and environmental sustainability. Ensuring that water is free from hazardous contaminants depends on water treatment, thereby preventing waterborne diseases such typhoid and cholera. Almost 2 billion people globally depend on unclean or contaminated water sources right now, underscoring a major public health issue that has to be given top priority.
2. Global current data on water and sanitation access
Globally, figures show that around 2.2 billion people lack access to safely regulated drinking water and almost 3.5 billion lack suitable sanitary facilities. In low-income areas especially, these shortcomings not only jeopardize health but also hinder economic growth and worsen inequality. Effective water treatment and sanitation systems are crucial for maintaining ecosystems, conserving resources, and assuring compliance with health regulations.
3. Article’s goal and article’s breadth
This article aims to investigate the worldwide situation of water treatment and sanitation by means of an analysis of policy frameworks, present issues, technological developments, and future forecasts. By studying these factors, the article seeks to provide a complete knowledge of the crucial role of water treatment and sanitation in accomplishing sustainable development goals and increasing quality of life worldwide.
Through this exploration, we seek to underscore the necessity for joint efforts among governments, NGOs, and communities to provide universal access to safe water and sanitation by 2030.
II. Global Water and Sanitation Landscape
Analysis of existing access levels to clean drinking water and sanitation
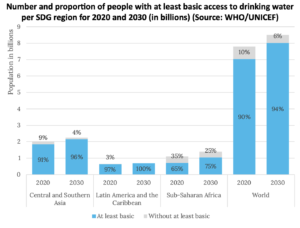
The global landscape of water treatment and sanitation reveals huge variations in access and quality, impacting billions of individuals. As of 2023, approximately 2 billion people lack clean drinking water, while 3.6 billion do not have access to safely managed sanitation facilities. These findings underline a major public health concern, particularly in low-income and rural communities where infrastructure is often inadequate or nonexistent.
1. Disparities in access across different regions (e.g., developed vs. poor countries)
Access to water and sanitation varies drastically between industrialized and underdeveloped countries. Most high-income nations have attained near-universal access to these vital services, although many underdeveloped countries struggle with basic provision. For instance, in 2022, only 59 nations achieved universal access to basic sanitation services, while in 55 countries, fewer than half the population had safely managed sanitation.
This gap underlines the urgent need for targeted investments and policy interventions in regions that lag behind.Urbanization and population increase further complicate the water and sanitation situation. The global urban population facing water scarcity is anticipated to double from 930 million in 2016 to between 1.7 billion and 2.4 billion by 2050.
2. Impact of urbanization and population growth on water supplies
Rapid urban expansion generally leads to increasing demand for water supplies, straining existing infrastructure and aggravating inequities in access. Additionally, extreme weather events connected to climate change are exacerbating water shortages, affecting both human health and agricultural productivity.The interplay of these variables needs a comprehensive effort to improve water treatment and sanitation globally.
Addressing the challenges of access and quality needs collaboration across governments, NGOs, and communities to create sustainable solutions that assure safe water and sanitation for all. Without coordinated efforts, the gap between those with access to clean water and sanitation and those without will continue to increase, perpetuating cycles of poverty and disease.
III. Challenges in Water Treatment and Sanitation
1. Major obstacles encountered globally, include infrastructural shortages, financial issues, and policy inadequacies

The challenges in water treatment and sanitation are varied and deeply established, affecting billions globally. One of the key problems is infrastructure deficiencies. Many places, particularly in developing countries, lack the basic facilities for proper water treatment and sanitation. Existing systems are typically antiquated or poorly maintained, resulting to inefficiencies and failures in service delivery. For instance, approximately 22% of healthcare facilities worldwide lack essential water supplies, substantially weakening healthcare quality and outcomes.
Funding issues further worsen these concerns. Many governments confront budget constraints that limit their ability to invest in new infrastructure or maintain old systems. The projected yearly cost of poor sanitation is around $223 billion, representing not just health expenditures but also lost productivity. Despite the economic benefits on investment in sanitation—where every dollar spent can generate up to five dollars in returns—funding remains insufficient to fulfill the requirements of vulnerable populations.
Policy gaps also restrict progress. In many cases, existing standards do not effectively deal with the complexities of modern water treatment and sanitation needs. There is often a lack of coordination among many parties, including government agencies, NGOs, and private sector organizations, which leads to fragmented approaches that fail to produce complete solutions.
2. The significance of climate change in increasing water scarcity and sanitation difficulties
Climate change greatly exacerbates water scarcity and sanitation challenges. Increasing temperatures and variable weather patterns lead to droughts and floods, straining already limited water resources. In 2020, 2.4 billion people lived in water-stressed countries, a scenario that is likely to increase as climate change progresses. These environmental changes not only affect water availability but also raise the risk of pollution, as flooding can overwhelm sanitary systems and contribute to outbreaks of waterborne diseases.
3. Health implications of poor water treatment and sanitation services
The health ramifications of inadequate water treatment and sanitation are catastrophic. Poor sanitation contributes to the mortality of over 800 children under five daily owing to avoidable diseases. The connection between unsafe water and health risks is well-documented; inadequate sanitation facilities lead to increased transmission of pathogens, resulting in significant morbidity and mortality rates.Addressing these challenges requires a concerted global effort focused on innovative solutions, increased funding, and robust policy frameworks that prioritize sustainable water management practices.
IV. Technological Innovations and Solutions
1. Overview of new technologies in water treatment (e.g., desalination, wastewater recycling)
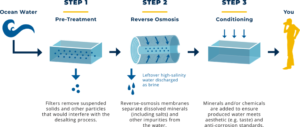
Technological advancements are altering water treatment and sanitation, addressing important concerns related with water scarcity and contamination. Emerging technologies such as desalination and wastewater recycling are at the forefront of these advancements.Desalination has evolved significantly, particularly with the introduction of low-energy reverse osmosis systems that reduce energy consumption while effectively removing salt from seawater.
Recent innovations include the use of carbon cloth electrodes, which efficiently remove boron from saltwater, a pollutant that previous approaches often ignore. This innovation not only enhances the quality of desalinated water but also reduces operational costs by up to 15%, making desalination a more viable solution for freshwater shortages in coastal regions. In addition to desalination, wastewater recycling technologies are gaining traction as sustainable solutions.
Techniques such as membrane bioreactors (MBRs) combine biological treatment with membrane filtration, allowing for high levels of purification while minimizing energy use. Furthermore, advanced oxidation techniques (AOPs) are being deployed to break down persistent contaminants, including pharmaceuticals, ensuring that treated wastewater can be safely reused for agricultural or industrial purposes.
2. Innovations in sanitation solutions (e.g., eco-toilets, biogas systems)
Innovations in sanitation are also noteworthy. Eco-toilets, which require less water and may transform human waste into compost or biogas, are becoming increasingly popular in locations without conventional sewage systems. These systems not only provide sanitation but also contribute to electricity production through biogas generation. This combined advantage highlights the potential of integrating waste management with renewable energy solutions.
3. Case studies of successful installations around the world
Several successful installations worldwide illustrate the usefulness of these technologies. For example, the Claude “Bud” Lewis Carlsbad Desalination Plant in California utilizes modern desalination processes to supply drinking water to nearly 400,000 persons, illustrating how innovative technology may address regional water scarcity. In India, decentralized wastewater treatment systems have been established in urban slums, providing people with safe sanitation options while promoting water reuse and decreasing pollution.
Overall, these technical improvements represent a big leap toward sustainable water management approaches. By harnessing advancements in water treatment and sanitation, we can address major global concerns connected to water scarcity and public health while paving the road for a more sustainable future.
V. Policy Frameworks and Global Initiatives
1. Examination of international frameworks (e.g., SDG 6) targeted at improving water and sanitation
The global environment for water treatment and sanitation is guided by numerous international frameworks, with Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6) being a cornerstone. Established by the United Nations, SDG 6 seeks to “ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all” by 2030.
This objective incorporates essential targets such as providing universal access to clean drinking water, proper sanitation, and hygiene, while also concentrating on improving water quality and encouraging sustainable water resource management. Despite the ambitious targets, progress continues alarmingly off-track, with 2.2 billion people lacking securely managed drinking water services and 3.5 billion without basic sanitation facilities.
2. Role of governments, NGOs, and commercial sectors in developing water treatment efforts
Governments, NGOs, and the corporate sector play crucial roles in encouraging water purification efforts. Governments are responsible for policy creation, infrastructure investment, and regulatory frameworks that promote access to clean water and sanitation. NGOs often bridge gaps by establishing grassroots activities that address local needs and campaigning for policy changes.
The private sector contributes through innovation, investment in technology, and collaborations that enhance service delivery. Collaborative efforts among these stakeholders are vital to mobilize resources and skills necessary to tackle global water and sanitation concerns.
3. Importance of community involvement and education in policy implementation
Community involvement is equally vital in the successful implementation of water and sanitation policy. Engaging local populations ensures that activities are culturally acceptable and adapted to individual needs. Education plays a critical role in this process; raising awareness about sanitary practices, the need of safe water, and the sustainable use of resources can empower communities to take control of local water management systems.
Programs that include community training on maintenance of water supply systems or sanitation facilities have shown increased sustainability and effectiveness.In summary, achieving SDG 6 requires a multi-faceted approach that includes robust international frameworks, active participation from various sectors, and strong community engagement.
As the globe grapples with rising water problems caused by climate change and population increase, concerted efforts towards these goals are more necessary than ever to secure access to safe water and sanitation for everyone.
VI. Future Scenarios for Water Treatment and Sanitation
1. Projections for global water treatment and sanitation by 2030 and beyond
As we move forward 2030 and beyond, the forecasts for global water treatment and sanitation are stark. Current statistics show that unless there is a dramatic acceleration in progress, billions will still lack access to adequate drinking water and sanitation facilities. The World Health Organization and UNICEF warn that obtaining universal access will need a sixfold increase in present efforts for drinking water, a fivefold increase for sanitation, and a threefold increase for hygiene services by 2030.
2. Ambition Levels: Business-as-Usual vs. High Ambition Scenarios
The scenarios for reaching these aims can be classified into two approaches: business-as-usual and high ambition. The business-as-usual scenario predicts that if current trends continue, many nations would fall short of fulfilling the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 6, which focuses on clean water and sanitation. This method often results in modest gains but fails to meet the pressing needs of vulnerable groups.
In contrast, high ambition scenarios include dramatic changes in policy, investment, and community engagement. These scenarios highlight integrated water resource management, innovative technologies, and increased funding channels. For instance, achieving high ambition involves not only more financial investment but also the adoption of sustainable methods such as wastewater treatment and rainfall collecting, which can greatly improve water availability.
3. Strategies for Enhancing Resilience Against Climate Change
To strengthen resilience against climate change impacts on water resources, various techniques are essential:
Integrated Water Resource Management (IWRM): Implementing IWRM at all levels ensures that water resources are managed holistically, taking into consideration the interconnection of water systems.
Investment in Infrastructure: Upgrading current infrastructure and investing in new technologies such as desalination and sophisticated wastewater treatment can help alleviate the consequences of climate variability.
Community Engagement: Involving local communities in decision-making processes encourages ownership and accountability, leading to more sustainable practices.
Policy Reform: Governments must develop policies that promote sustainable water management techniques and incentivize innovation in the industry.
Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about water conservation measures can empower individuals to contribute to sustainable water use.
VII. Conclusion
In conclusion, while the problems facing global water treatment and sanitation are enormous, embracing high ambition policies can pave the path for a future where safe water and sanitation are accessible to all. The next decade is important; without rapid action, the gap between those with access to clean water and those without will continue to increase, worsening health risks and socio-economic inequality.
Summary of main conclusions from the article
The global picture for water treatment and sanitation displays a severe dilemma that impacts billions of people. Despite significant advances, approximately 2 billion individuals still lack access to safely regulated drinking water, and 3.6 billion do not have basic sanitation services.
This article has emphasized the important challenges encountered in this sector, including infrastructural inadequacies, financial issues, and the worsening effects of climate change. It has also underlined the necessity of technology breakthroughs and coordinated efforts among governments, NGOs, and communities to solve these concerns successfully.
Call to action for stakeholders at all levels to prioritize water treatment and sanitation
As we move towards 2030, meeting the targets outlined by Sustainable Development Goal 6 demands urgent action from all parties. Governments must prioritize investment in infrastructure and policy reforms that facilitate sustainable water management practices. NGOs play a critical role in executing grassroots initiatives and advocating for neglected populations.
The business sector can assist through innovation and investment in new technologies that enhance service delivery. Importantly, community involvement is vital; empowering local populations via education and engagement ensures that solutions are relevant and durable.
Vision for a sustainable future with fair access to clean water and sanitation for everyone
The vision for a sustainable future rests on fair access to clean water and sanitation for all. This future is achievable if we collectively commit to high ambition strategies that prioritize resilience against climate change impacts, integrated resource management, and inclusive policies.
By working together—across sectors and borders—we can close the gap in access to safe water and sanitation, ultimately improving health outcomes, stimulating economic development, and promoting social equity.In conclusion, the moment for action is now. Let us join our efforts to guarantee that every human has access to safe drinking water and proper sanitation, paving the path for a healthier, more sustainable world for generations to come.
FAQs
How does urbanization effect water scarcity in various places
Urbanization considerably increases water demand in regions, resulting to scarcity, especially in developing nations where fast city growth typically outpaces infrastructure development, leaving millions without access to safe drinking water or sanitation facilities.
What are the key challenges in obtaining universal access to clean drinking water by 2030
Achieving universal access to safe drinking water by 2030 faces problems such as limited infrastructure, financial constraints, climate change impacts, and increasing urban population increase, which stresses existing water supplies and services.
How does the task of water collection influence women and girls in rural regions
The burden of water collection disproportionately impacts women and girls in rural regions, sometimes constraining their time for education and economic pursuits, and may expose them to health hazards and abuse during collection trips.
What initiatives are being implemented to enhance sanitation in undeveloped countries
Strategies to enhance sanitation in poor nations include community-led efforts, investment in infrastructure, promotion of hygiene education, and public-private partnerships to assure sustainability and accessibility of sanitation services.
How does climate change increase water and sanitation inequality globally
Climate change exacerbates water and sanitation inequities by increasing the frequency of extreme weather events, leading to additional water scarcity and reducing the quality and availability of water resources particularly in vulnerable communities.




“Thanks for sharing such valuable information!”
“This article is real
“Amazing post, keep up the good work!”
“This is exactly what I was looking for, thank you!”
“I appreciate the detailed explanation, very helpful!”
“Amazing post, keep up the good work!”
“This is exactly what I was looking for, thank you!”
“Great content, learned a lot from this post!”