Table of Contents
Toggle carbon balance has to be struck between carbon credits and carbon offsets
carbon balance has to be struck between carbon credits and carbon offsets
A. Introduction to carbon offsets and credits
Carbon credits and carbon offsets have become important mechanisms among the many approaches to dealing with this worldwide catastrophe. These resources provide doable solutions to lower the total carbon footprint of people, businesses, and even entire nations.
Our combined efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions can be greatly advanced by knowing about and using carbon credits and carbon offsets.
Permits known as carbon credits let their holders release a certain volume of greenhouse gasses, such as carbon dioxide. One metric ton of carbon dioxide is equivalent to one carbon credit. This implies, a carbon credit represents one tonne of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) that has been avoided or removed from the atmosphere.

The idea is to implement a cap-and-trade system where companies can trade credits to meet their needs while keeping total emissions within a set limit. Because businesses can sell their extra credits to people who need them more, this system offers financial incentives for lowering emissions.
Conversely, carbon offsets are investments made in initiatives to lessen or eliminate greenhouse gas emissions from the atmosphere. Among these projects might be methane capture, renewable energy projects, and reforestation.
An organization that acquires carbon offsets funds these initiatives to make up for their emissions, therefore balancing their carbon footprint.
B. Carbon Credit and Offset Roles
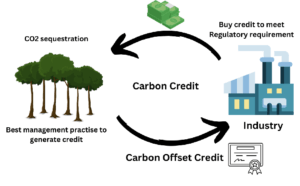
Carbon credits and carbon offsets significantly bolster the promotion of sustainable practices across various sectors. They motivate business to invest in and innovate with greener technology and procedures. These processes also help to develop projects involving conservation, renewable energy, and other measures to lower emissions worldwide.
Businesses can not only satisfy legal requirements but also improve their corporate social responsibility and attract environmentally concerned customers by including carbon credits and carbon offsets in their operations. The move to a more low-carbon and sustainable economy depends critically on these instruments.
Finally, carbon offsets and credits are crucial elements of the worldwide plan to address climate change. They offer practical means of lowering greenhouse gas emissions and advancing sustainable development, therefore opening the door to a more robust and healthy earth.
C. What are Carbon credits?
The battle against climate change heavily relies on carbon credits. They basically permit the holder to release one metric ton of carbon dioxide or an equivalent quantity of another greenhouse gas.
As part of global carbon trading markets, these credits provide a financial incentive for businesses and nations to cut their emissions. Carbon credits are prices on carbon emissions that encourage companies to use greener methods and technologies to reduce their carbon footprint.
D. Origin and Purpose of Carbon Credits
The Kyoto Protocol is the international agreement that established carbon credits. It was signed in 1997 and came into force in 2005. Carbon credits were proposed as a market-based method to accomplish the Kyoto Protocol’s global reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
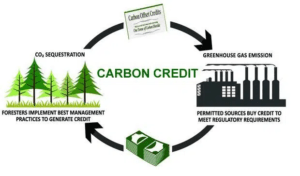
Carbon credits are primarily used to offer financial incentives for cutting emissions. Giving a carbon dioxide emission a financial value motivates companies and governments to look for economical methods to reduce their emissions.
E. How Carbon Credits Work
The mechanism behind carbon credits is cap-and-trade. Governments or regulatory agencies cap the emissions of greenhouse gases from industries or sectors.
Then, a set amount of credits that stand for the permitted emissions are assigned to the companies. Should a business emit less than allowed, it may sell the extra credits to other businesses that go above their allocated number. Companies are given the freedom to manage their emissions economically, while the overall emissions are guaranteed to stay under the predetermined cap.
F. Types of Carbon Credits
1. Compliance Credits
Entities subject to mandatory emission reduction targets established by regulatory bodies employ compliance credit. Many times, these credits are included into national or international climate laws and are exchanged on controlled markets. Compliant credits guarantee that businesses follow legally required emission limitations and support both national and international reduction targets.
2. Voluntary Credits
On the other hand, voluntary credits are purchased by individuals, businesses, or organizations who choose to reduce their emissions as part of their dedication to environmental responsibility, even without legal mandates to do so.
Trading in voluntary markets, these credits frequently fund a broad spectrum of carbon reduction initiatives. Entities may show their dedication to sustainability and balance their carbon footprint by acquiring voluntary credits.
G. What is a carbon offset?
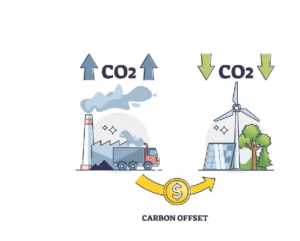
One way to make up for greenhouse gas emissions is to finance initiatives that lower or eliminate an equivalent quantity of emissions elsewhere.
An organization effectively invests in carbon-reducing projects when it buys carbon offsets, such as methane capture projects, reforestation projects, or renewable energy installations.
A net-zero carbon footprint is the intended result of balancing out the emissions generated by the organization.
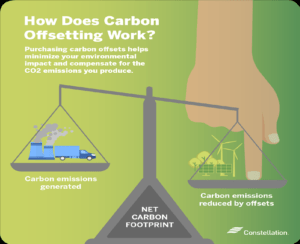
1. The Mechanism of Carbon Offsets
Carbon offsets work by figuring out how much pollution a company produces and then funding initiatives that would either sequester or reduce that much. These initiatives can range greatly in scope from building solar power plants to planting trees. Through funding these initiatives, the organisation makes sure that its emissions are balanced, which helps to lower emissions generally.
H. Carbon offset project types
1. Projects Using Renewable Energy
Projects for renewable energy seek to replace energy sources based on fossil fuels with sustainable, clean options, including hydro, solar, and wind power. Through energy generation without using fossil fuels, these initiatives drastically lower greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Projects About Land Use and Forestry
Projects related to forestry and land use center on afforestation, reforestation, and forest conservation. Because trees take up carbon dioxide, these initiatives effectively sequester carbon and slow down climate change. Important tactics in these efforts are planting new trees and preserving the ones that already exist.
3. Projects Toward Energy Efficiency
Enhanced energy performance of appliances, industrial processes, and buildings is the goal of energy efficiency programs. These initiatives contribute to the decrease of emissions by lowering the amount of energy needed. Upgrades to insulation, energy-efficient lighting installations, and energy-efficient industrial operations are a few examples.
4. Methane Capture Projects
Methane capture programs seek to lower emissions of this powerful greenhouse gas. Using methane as an energy source, these initiatives can capture it from landfills, agricultural operations, and wastewater treatment plants and keep it out of the sky.
I. Carbon Offsets vs. Carbon Credits

Though they work differently, carbon offsets and credits both have as their goal lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Usually included in regulated markets with required reduction targets, carbon credits are trading permits to emit carbon dioxide.
Conversely, carbon offsets are typically part of volunteer work and entail sponsoring certain initiatives that lower or sequestrate emissions. While carbon offsets concentrate on making up for emissions through specific projects, credits are primarily about trading within a cap and compliance.
J. Purchase Instructions for Carbon Credits and Carbon Offsets

Acquiring carbon offsets and carbon credits requires a number of procedures. Buyers must initially specify their objectives for reducing emissions as well as the kind of credits or offsets they need.
They can thereafter buy them from brokers, exchanges, or internet sites that focus on carbon trading. To guarantee the legitimacy and efficacy of credits or offsets, they must adhere to specific criteria and undergo validation by reputable external organizations.
1. Evaluating the Carbon Credits and Carbon Offsets Quality
Not every offset and carbon credit is created equally. Good credits and offsets ought to be extra, meaning that they lower emissions in ways that would not have happened without the money.
In addition, they ought to be observable, guaranteeing that the cuts are actual and quantifiable as well as long-lasting, i.e., emission reductions. To assess the quality, one must look into the history, the criteria the project satisfies, and the verification procedure it has gone through.
2. The role of verification Carbon credits and carbon offsets:
One essential element of the market for carbon credits and carbon offsets is verification. A third party verifies that the claimed emission reductions are accurate, quantifiable, and align with established criteria.
In this procedure, outside auditors evaluate the reporting, monitoring, and methodology of the project. Buyers are guaranteed to be actually reduce emissions by the confidence and trust that come from verified credits and offsets.
3. Carbon credits’ and carbon offsets’ economic effects
Offsets and credits for carbon can be rather beneficial economically. They encourage new sectors like renewable energy to expand, provide financial incentives for companies to innovate and use cleaner technologies, and create jobs in the green economy.
They can also support businesses in reducing emissions and managing regulatory risks, therefore enhancing their competitiveness in the market.
K. Regional Carbon Credits and Carbon Offsets
1. North America
Carbon markets are well-established in North America, most notably in California with its cap-and-trade scheme. The initiative has effectively cut emissions and sparked clean energy investments. Voluntary markets are expanding as more businesses and people want to leave less of a carbon footprint.
2. Continental Europe
Europe has led the way in carbon markets; the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) is the biggest carbon market in the world. The EU ETS has achieved notable emission reductions across various industries and remains a benchmark for regions seeking to implement similar systems.
3. East Asia
Asia is opening up its carbon markets quickly; nations like China and South Korea are putting national and regional plans into place. Launched in 2021, China’s national carbon market is expected to become the biggest in the world, including important industrial sectors and seeking to reduce emissions from the biggest emitter in the world.
L. Successful Carbon Offset Project Case Studies
1. Conservation of Amazon Rainforest
One excellent illustration of a carbon offset program gone right is the conservation project for the Amazon rainforest. The initiative leads to significant carbon dioxide sequestration and wildlife preservation, safeguarding extensive areas of the Amazon. By offering substitute means of subsistence free from deforestation, it also benefits the local population.
2. Projects in Solar Power in India
Initiatives involving solar power have been crucial in India in lowering emissions and supplying sustainable energy. Large-scale solar farms and rooftop solar installations, for example, have supplanted fossil fuel-based energy sources, reducing emissions and providing energy to isolated and underdeveloped regions.
M. The Carbon Credits and Carbon Offsets Market’s Challenges
Carbon credits and carbon offsets have various problems, even with their advantages. Market volatility, regulatory ambiguity, and the risk of fraud can undermine the credibility and effectiveness of these systems. Maintaining the integrity of the market and addressing these problems need transparency, strong verification procedures, and uniform regulatory frameworks.
1. Carbon Credit and Offset Futures
As commitment to lowering emissions grows worldwide, the future of carbon credits and carbon offsets appears bright. Improved regulatory systems, more funding for environmentally friendly initiatives, and technological breakthroughs will probably make these instruments more powerful and accessible. High-quality carbon credits and carbon offsets should become more in demand as nations and businesses establish more ambitious climate goals.
N. How Businesses can benefit from Carbon Credits and Carbon Offsets
Carbon offsets and credits have several uses for businesses. Businesses that incorporate these systems into their operations can lower their carbon footprints, meet legal obligations, and improve their standing with investors and customers who value sustainability.
Better energy efficiency and the use of cleaner technology can also spur innovation and cost reductions through investments in carbon credits and carbon offsets.
O. Conclusion: The Road Ahead for Carbon Credits and Carbon Offsets
Carbon credits and carbon offsets will become increasingly important to the worldwide attempts to slow down climate change. Businesses, governments, and individuals can all help to significantly reduce emissions by knowing their principles and using them well.
Through these methods, one of the most urgent problems of our day can be practically and scalablely addressed, opening the door to a more robust and sustainable future.
FAQs
What are the basics of carbon credits and carbon offsets?
While investments in projects that lower emissions abroad to offset one’s own emissions are known as carbon offsets, carbon credits are reductions in greenhouse gas emissions attained through initiatives like reforestation.
How do carbon credits contribute to environmental sustainability?
Contributing greatly to environmental sustainability goals, carbon credits encourage businesses to cut emissions, make investments in clean technologies, and back sustainable initiatives like forest preservation and renewable energy.
What is the difference between carbon credits and carbon offsets?
While carbon offsets fund programs that lower emissions elsewhere, carbon credits directly lower emissions, giving companies a means of lessening their environmental effect.
How can businesses benefit from understanding carbon credits?
Effectively understanding and using carbon credits can help businesses attract environmentally concerned clients, comply with legislation, increase operational efficiency, and get cash rewards.
What are some examples of successful carbon offset projects?
Projects for methane capture, afforestation, renewable energy installations, and energy efficiency that have successfully lowered greenhouse gas emissions have all been successful carbon offset projects.
How are carbon credits regulated on a global scale?
Along with regional carbon markets and norms that guarantee credibility, openness, and accountability in carbon trading, international agreements such as the Kyoto Protocol and Paris Agreement govern carbon credits.
What role do carbon offset markets play in mitigating climate change?
Carbon offset markets serve to achieve global climate change mitigation targets, support sustainable behaviors, foster innovation in clean technologies, and facilitate investments in emission reduction initiatives.
What are the key challenges associated with implementing carbon credit programs?
Accurate baseline emissions are a challenge, as are project additionality, verification of carbon reductions, fraud prevention, social and environmental co-benefits, and market stability.
How can individuals participate in carbon offsetting initiatives?
Participating individuals can calculate and offset their carbon footprint, back verified carbon offset projects, cut their own emissions, support climate legislation, and encourage sustainable living.
What are the environmental impacts of utilizing carbon credits and carbon offsets?
Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, better air quality, ecosystem and biodiversity preservation, and promotion of sustainable development can all result from the usage of carbon credits and carbon offsets.
How do carbon credits contribute to corporate social responsibility efforts?
Carbon credits show a dedication to environmental care, help achieve sustainable development objectives, improve brand reputation, involve stakeholders, and correspond with morally and responsibly run businesses.
What are the future trends in the carbon credit and offsetting industry?
Future developments include rising demand for carbon credits, growing carbon markets, new offsetting technologies emerging, integrating carbon pricing systems, and putting more emphasis on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) projects.





[…] Knowing LEED certification is absolutely essential for anyone working in construction. It entails a thorough procedure that requires cooperation, careful planning, and strict adherence to standards. This book is to give a complete knowledge of LEED certification, stressing its relevance, advantages, and the processes required to reach it. Whether your field of expertise is architecture, engineering, construction, or development, this book will provide the tools you need to negotiate LEED certification’s complexity and apply sustainable ideas to your projects. […]